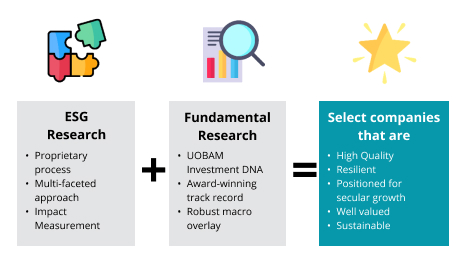
Investors are increasingly applying non-financial factors as part of their analysis process to identify material risks and growth opportunities.
Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) – an earlier model typically using value judgments and negative screening to decide which companies to invest in.
ESG investing – grew out of the SRI investment philosophy and as a more modern take, involves looking at finding value in companies—not just at supporting a set of values, by incorporating intangibles into traditional financial analysis.
ESG – stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance and summarise a variety of factors that are financially material to businesses, and these include (but are not limited to):
|
Environmental
|
Social
|
Governance
|
- Climate change policies
- Carbon footprint
- Renewable energy
- Waste management
- Pollution (air, water etc.)
|
- Employee treatment; training; safety
- Gender and diversity
- Customer satisfaction
- Child and forced labour
- Product safety record
|
- Executive compensation, bonuses
- Corruption
- Transparency and disclosure
- Board accountability
|
From an investment standpoint, the integration of ESG within an investment strategy helps to form the foundation of what we term as ESG Investing. In general, due to its popular adoption by asset owners and managers, ESG investing has become synonymous with sustainable investing.